Chapter 9 Introduction to Ramp Metering
9.1 What is Ramp Metering?
Signals placed at end of on-ramps to regulate the flow of on-ramp traffic onto the freeway. Vehicles queued at the signal are served one at a time (i.e., one vehicle per green indication)
- Typically operate during peak traffic flow periods
- Typically operated by state agency (e.g., FDOT)
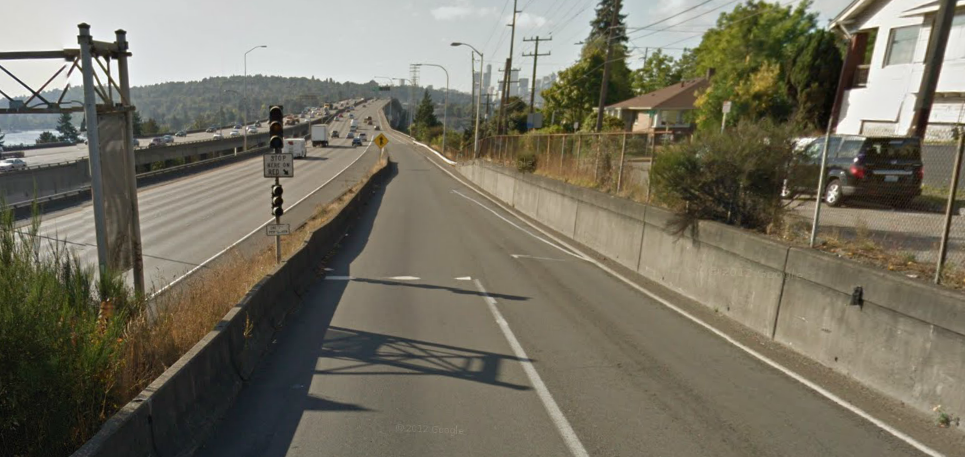

Figure 9.1: Ramp Meter (Signal): I-5, Seattle just north of downtown

Figure 9.2: Ramp Meter

Figure 9.3: Ramp Meter
9.2 Why Meter Ramps?
- To reduce or prevent mainline congestion
- Keep freeway running at or near capacity for longer periods of time
- Discourage short freeway trips
- Improve safety on mainline by reducing frequency of stop-and-go traffic conditions
- Improve merge safety
- Break up merging platoons
- Decrease side-swipe and rear-end accidents
9.3 Consequences of Ramp Metering
- Queuing at ramps
- Driver diversion to other routes
- Driver diversion to other modes
- Driver diversion to other times of day
9.4 Ramp Metering Hardware/Infrustructure
Typical Detector Configuration
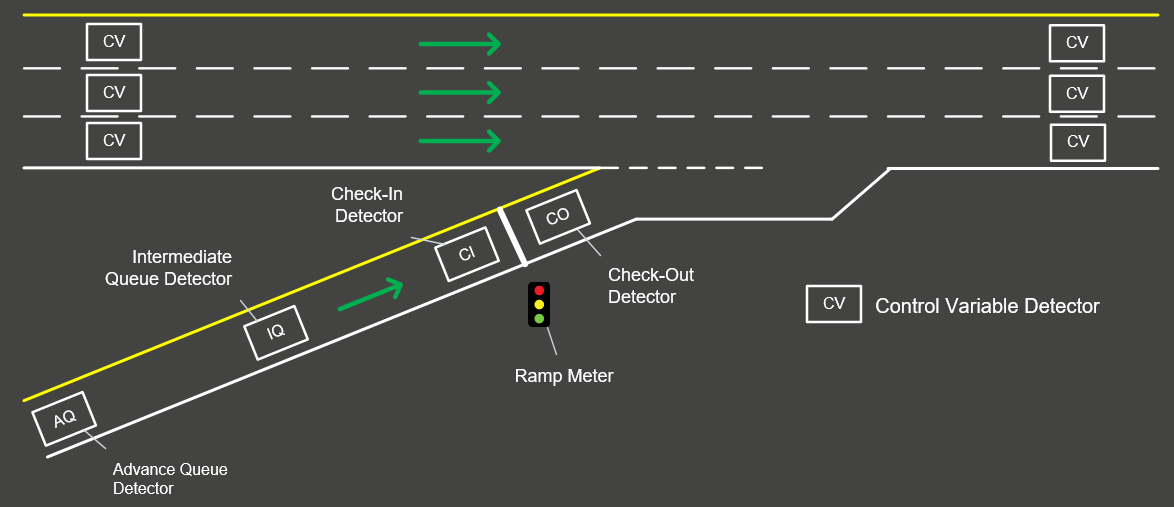
Figure 9.4: Typical Detector Configuration
Typical Ramp Hardware
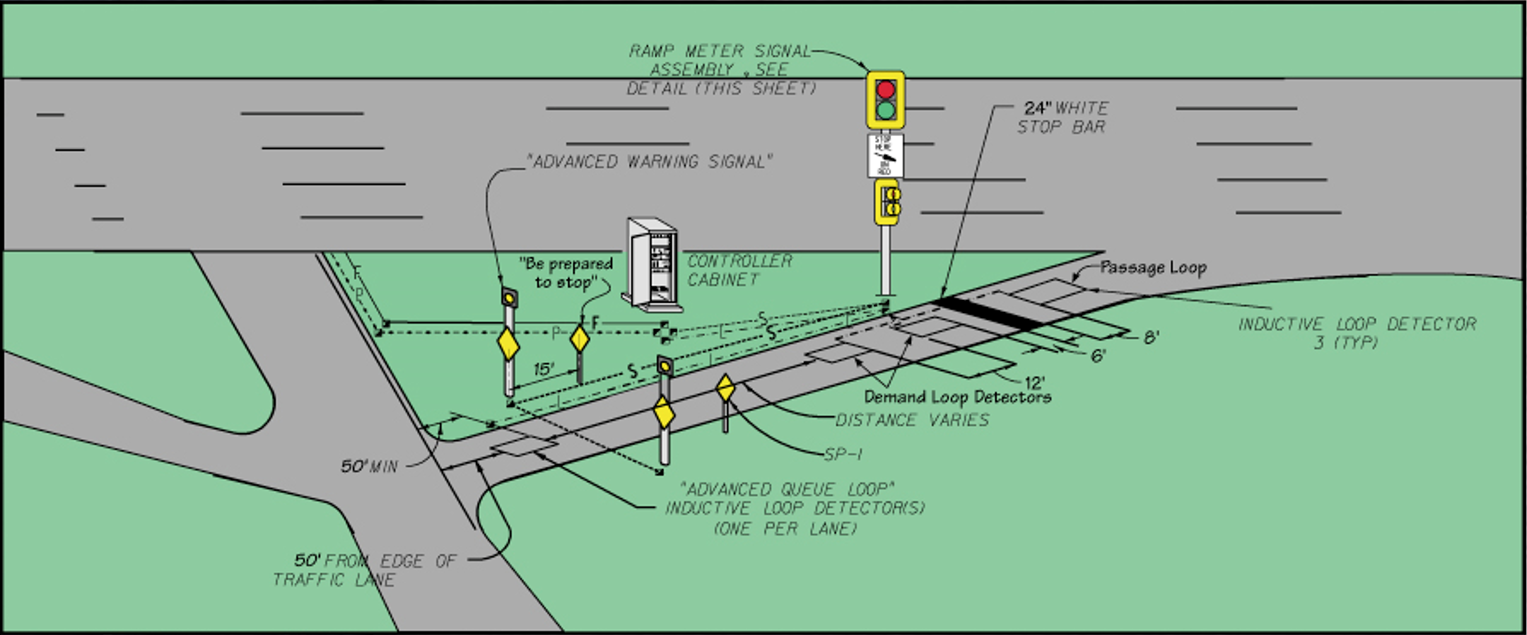
Figure 9.5: Typical Ramp Hardware
Typical Signal Display
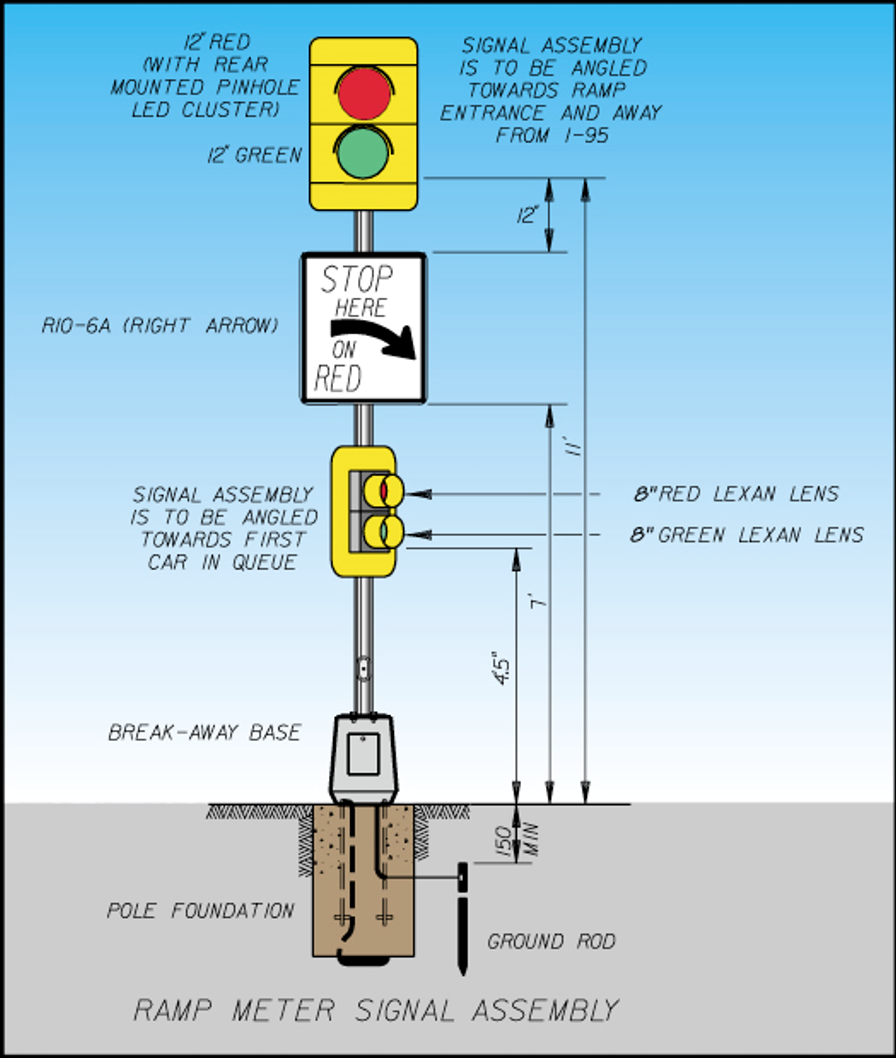
Figure 9.6: Typical Ramp Metering Signal
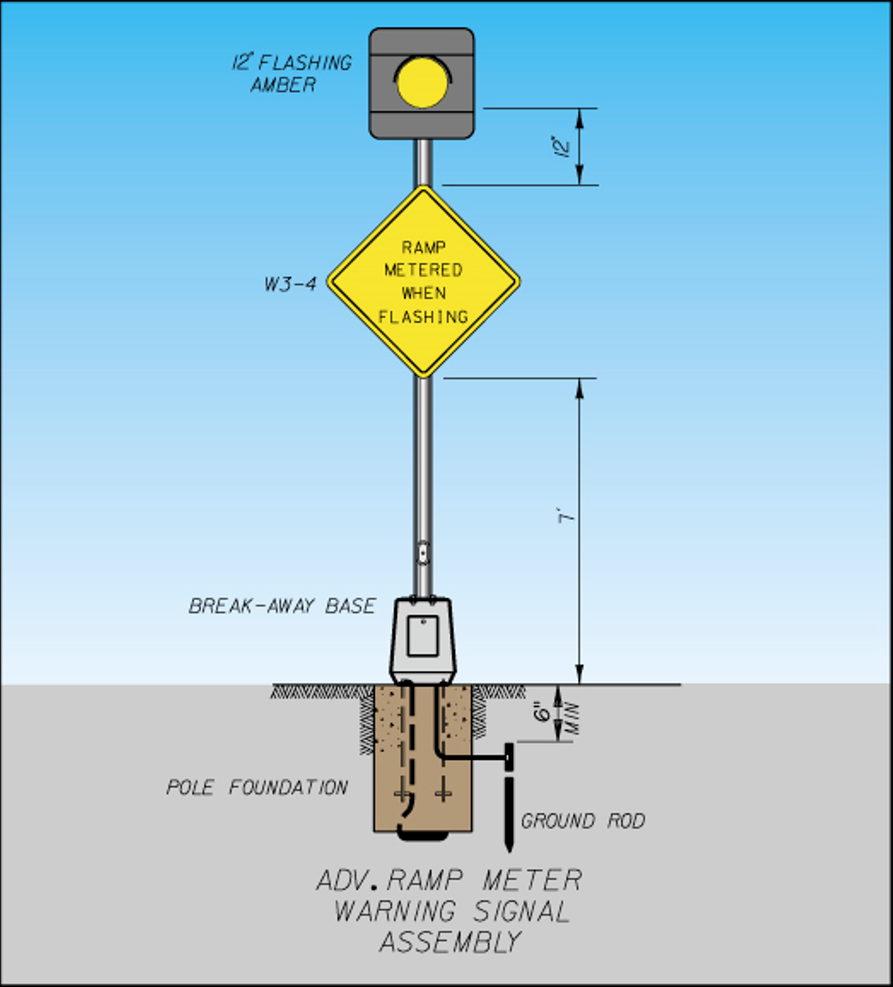
Figure 9.7: Advance Warning Display
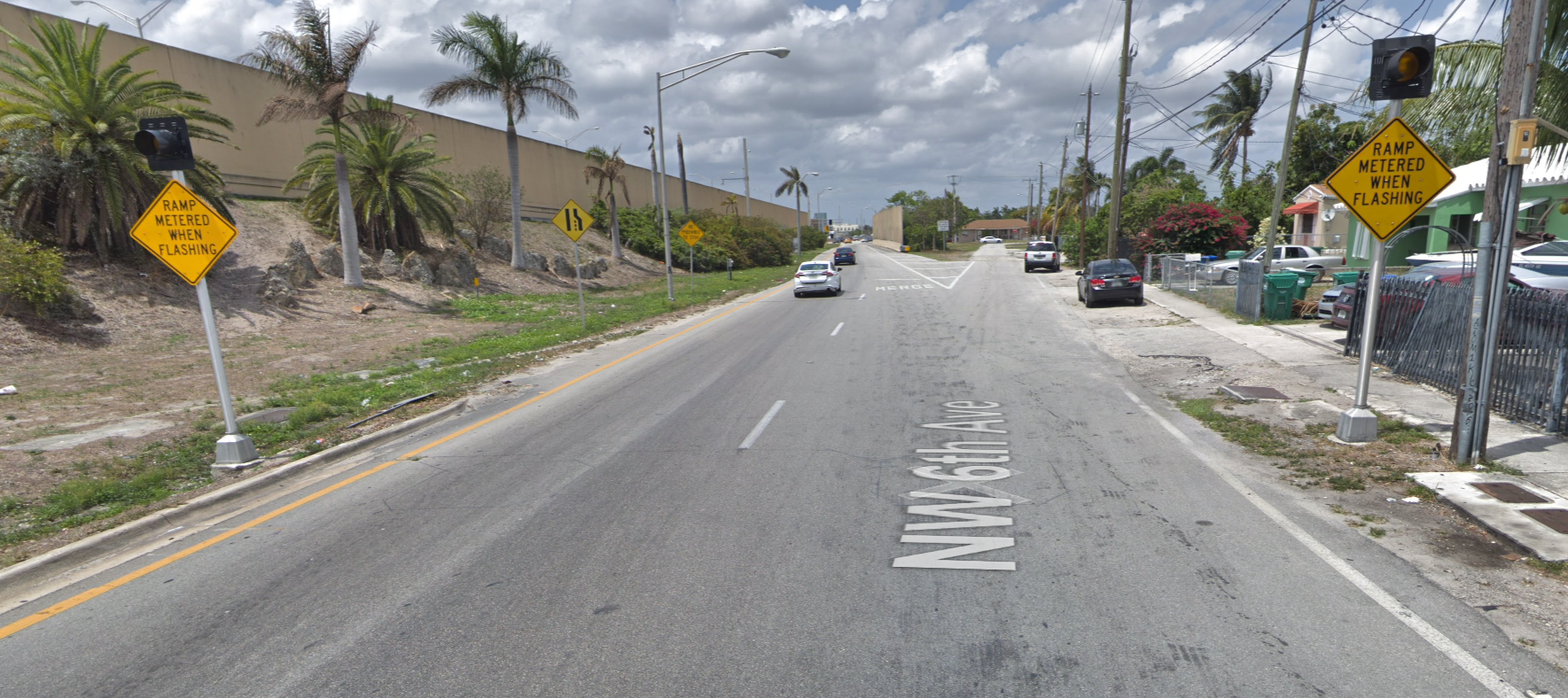

Figure 9.8: Miami: I-95/NW 6th Ave
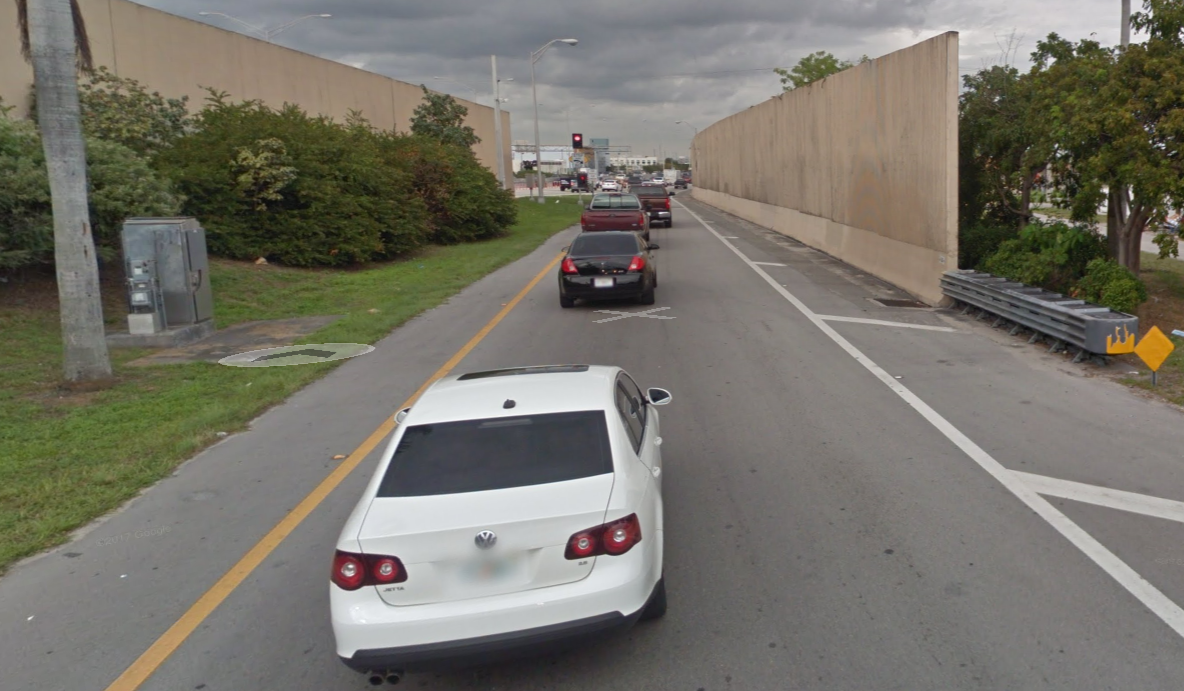

Figure 9.9: Miami: I-95/NW 81st St
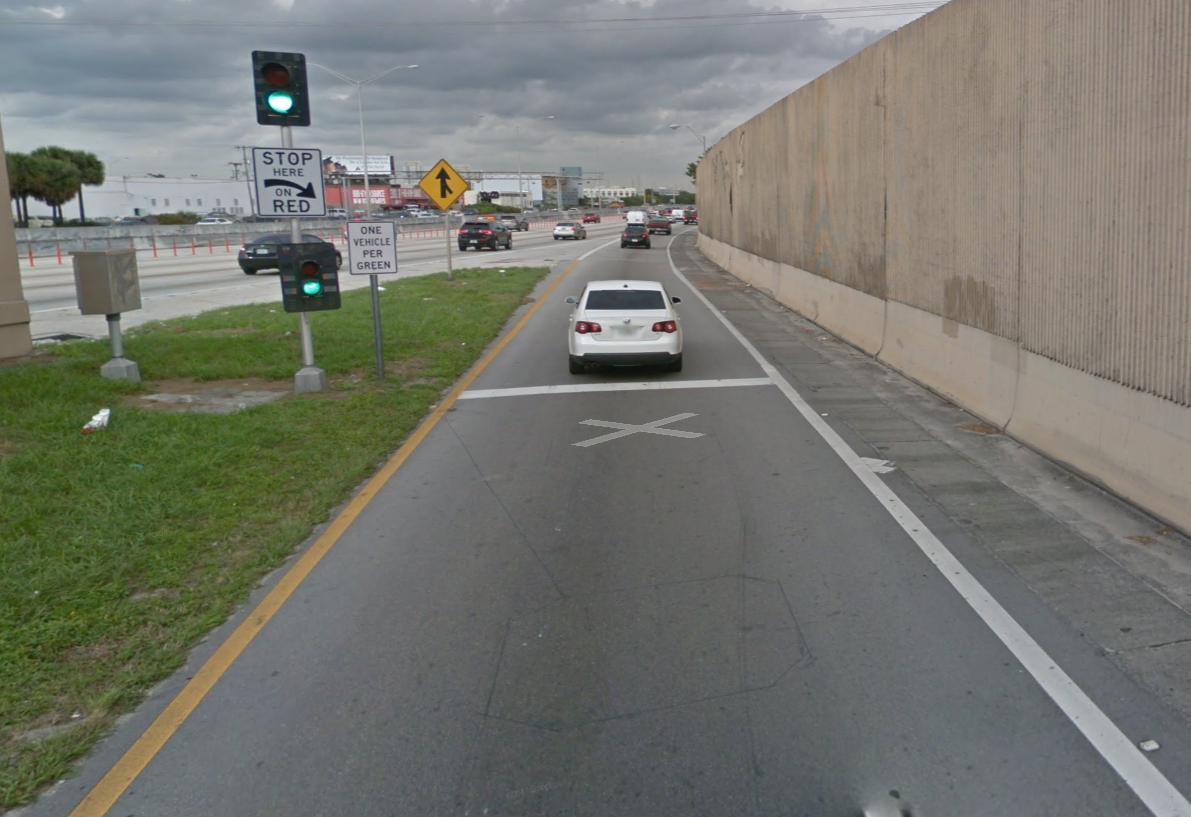

Figure 9.10: Miami: I-95/NW 81st St

Figure 9.11: Multilane Metering (California)
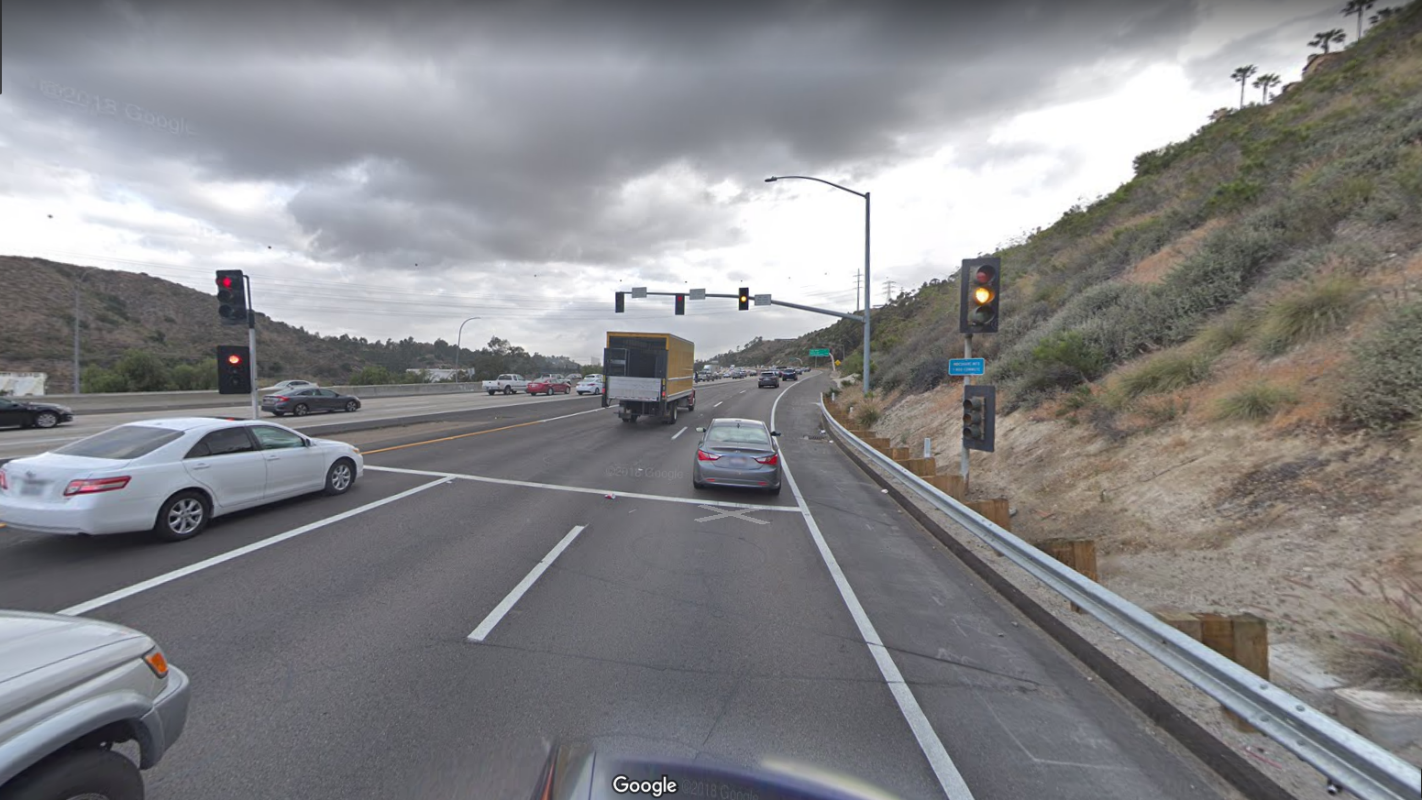

Figure 9.12: Multilane Metering (California)
9.5 Example Ramp Meter Control Strategies
9.5.1 Ramp Closure
- Manually placed barriers
- Automated barriers
- Signing
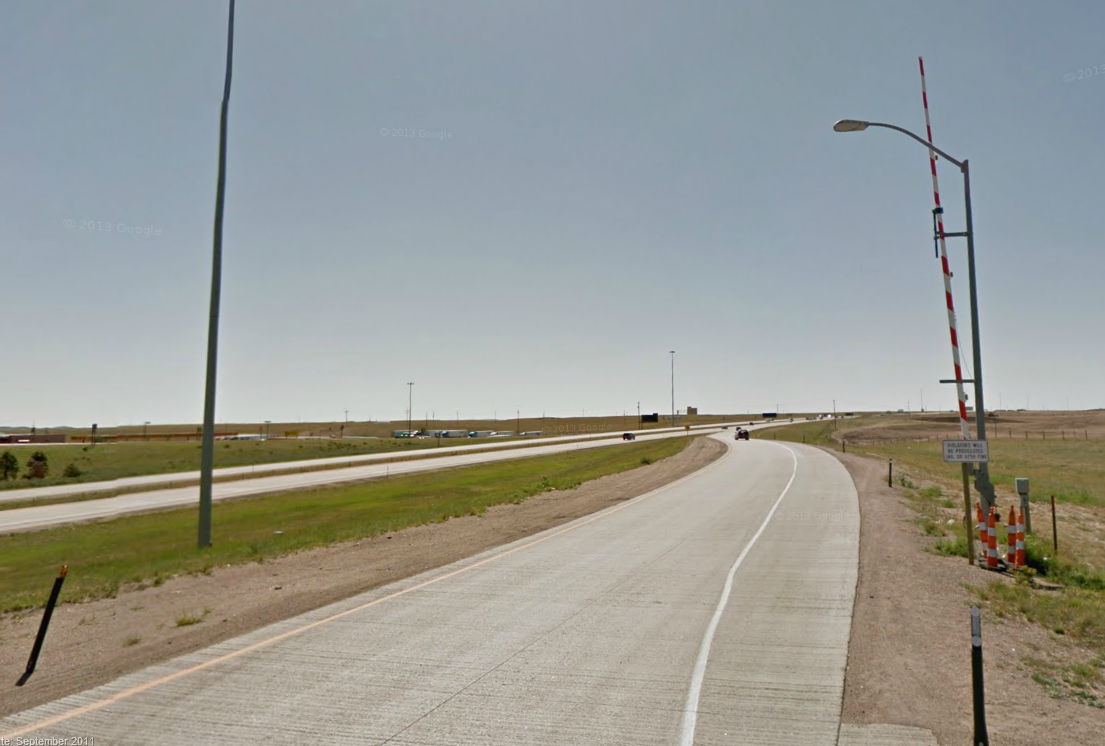

Figure 9.13: I-25, between Cheyenne and Denver
Advantages
- Inexpensive and Easy
Disadvantages
- Could result in unused mainline capacity
- May cause undesirable diversion
- Will not win any popularity contests
9.5.2 Pre-Timed
- Metering rate not directly influenced by mainline traffic conditions
- Determination of metering rates from historical traffic counts
- Often consists of different programs for different times of day
Advantages
- Relatively easy to implement
- No detection necessary
Disadvantages
- Cannot efficiently address day-to-day variations
- Cannot account for non-recurring congestion
9.5.3 Traffic Responsive
- Metering rate is a function of mainline traffic conditions
- Metering rate updated every 30-60 seconds
Advantages
- Better utilizes available mainline capacity
- Usually lower ramp delay
Disadvantages
- Needs mainline detectors
9.5.4 Gap Acceptance
- Sensors upstream in outside lane detect gap sizes
- When adequate size gap is detected, ramp vehicle is released to merge into this gap
- Used in conjunction with speed detector
- If traffic is congested, use minimum metering rate
Advantages
- Safe merge condition likely
- Possible lower travel time from meter to merge point (less speed adjustment by merge vehicle)
Disadvantages
- More irregular metering operation pattern
- Longer queue delays
- Does not utilize freeway capacity as effectively
9.6 Practical Considerations
- Ramp Queuing Storage
- HOV Bypass Lanes
- Minimum/Maximum Metering Rates
- Violation Enforcement
- Equity Issues
- Detection Capabilities
- System Capabilities
9.6.1 Ramp Queuing Storage
Have to account for possibility of ramp overflowing to upstream intersections if storage is inadequate.
Some agencies respond by discharging ramp (i.e., usually set to maximum metering rate)
- This counteracts metering strategy
9.6.2 HOV Bypass Lanes
HOV bypass lanes allow carpool vehicles enter freeway without stopping for ramp meter. A separate lane is provided so that ramp queue can be completely bypassed. This will potentially encourage carpooling, with or without mainline HOV lanes.
This complicates metering scheme because this uncontrolled volume has to be taken into account.
If you cannot enforce, usually will create more problems than it solves.

Figure 9.14: Ramp Meter with HOV bypass

Figure 9.15: Ramp Meter with HOV bypass
9.6.3 Min/Max Metering Rates
Maximum
- Typically around 900 veh/h (15 veh/min)
- This corresponds to a maximum practical discharge rate of 1 vehicle every 4 seconds
Minimum
- Typically between 180 to 240 veh/h (3 to 4 veh/min)
- Anything less than this and many motorists will think the signal is broken and then violate
9.6.4 Violation Enforcement
There WILL be violators.
- Extent of violation will be directly linked to motorists’ perception of level of enforcement
- This will be compounded if HOV bypass lane has high violation rate
Violations still have to be factored into metering scheme/algorithm.
Be prepared for major public perception problems if enforcement is inadequate.
- Also, violations will beget more violations
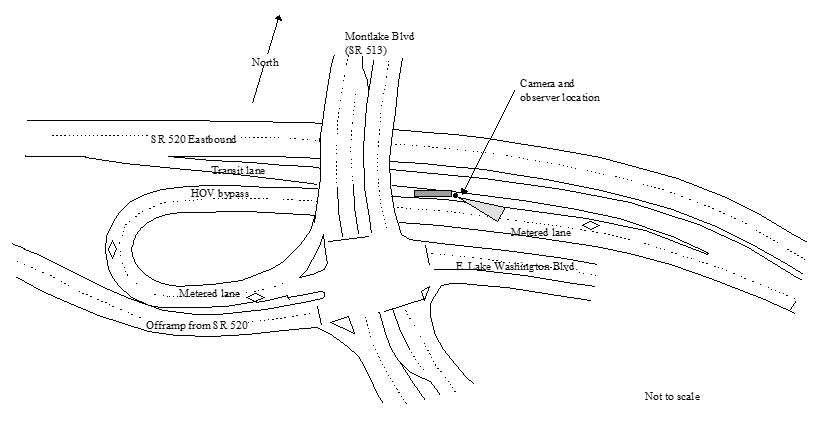
Figure 9.16: HOV Bypass, 47.6439888, -122.3045164

Figure 9.17: HOV Bypass
9.6.5 Equity Issues
Very undesirable to have large disparity between metering rates of adjacent on-ramp meters
- Motorists will figure it out and complicate your metering scheme/algorithm